Cross border Compliance Observation | "Extreme Sanctions" Against Russia by the United States and Europe, Analysis of Chinese Enterprises' Response Strategies [Going Global Think Tank]
CLICK THE BLUE WORD TO FOLLOW US

Go out to think tanks and observe
With the intensification of the Russia-Ukraine conflict, the United States has been increasing its sanctions against Russia, while also putting pressure on China. A few days ago, White House Press Secretary Pasacki declared that if China did not sanction Russia, the United States would probably retaliate against China. Even during the high-level meeting between China and the United States in Rome, American National Security Advisor Sullivan also asked China not to provide economic and material assistance to Russia.
Lawyer Guo Huan, a special legal expert at the Going Global Think Tank (CGGT) and partner at Kindu Law Firm, pointed out that China and Russia have established a close strategic partnership since 2014. For Chinese companies, especially those with close trade ties with Russia and financial institutions, special attention should be paid to Russian regulation and sanctions to avoid major transactions or substantive assistance with sanctioned Russian entities, As a result, it is seen as "avoiding" the risk of triggering sanctions.
How can Chinese enterprises cope with the risk of sanctions related to Russian businesses? Today, CGGT publishes analytical articles by Guo Huan, Zhou Xinyu, and Chen Qichao for readers who are interested in cross-border compliance management.
main points
CGGT,CHINA GOING GLOBAL THINKTANK
1. Recently, with the escalation of the conflict between Russia-Ukraine conflict, the United States has successively issued two administrative orders and four related directives against Russia, and continues to issue sanctions laws and regulations against Russia. The scale, frequency, and scope of deterrence of this sanctions, as well as the extensive implementation of sanctions in collaboration with allies, are the extreme characteristics presented by the US economic sanctions in the context of this war.
2. In 2021, the trade volume of goods between China and Russia reached 146.87 billion US dollars, ranking steadily as Russia's largest trading partner for 12 consecutive years. Among the goods exported by China to Russia in 2021, the top 20 include handheld wireless telephones, automatic data processing equipment, fur clothing, toys, electrical equipment, LCD display panels, small buses, compressors, valves, and lighting devices.
3. The risk identification of the actual business content is the core, which may include but not limited to the identification of import and export trade item risks, confirmation of upstream and downstream partner blacklists, and risk sorting of trading countries and industry sectors. At the same time, commercial and legal risks should be comprehensively considered in conjunction with business scenarios.
Main text
CGGT,CHINA GOING GLOBAL THINKTANK
Wen/Guo Huan, Zhou Xinyu, Chen Qichao
preface
Since the escalation of the conflict between Russia and Ukraine on February 21, 2022, multiple countries such as the United States and Europe have launched a series of export control and economic sanctions measures in areas crucial to Russia's national economy, including defense, energy, finance, trade, telecommunications, transportation, etc., which can be called unprecedented "extreme sanctions". These extreme sanctions further exacerbate geopolitical risks and will also bring more uncertainty to the fragile global supply chain system that was originally affected by the pandemic.
This article will be based on the current international situation, conduct corresponding deduction and analysis of hot sanctions measures taken by the United States and Europe against Russia, explore the potential impact of such sanctions on Chinese enterprises, and provide certain response ideas for relevant enterprises.
Part One: A Brief History and Current Hot Spots of US and European Sanctions Against Russia
1、 The sanctions imposed by the United States and Europe on Russia have a long history
Economic sanctions, as the core of US foreign policy, have mostly been applied to Iran, China, and even Russia in the current round of sanctions against Russia, despite their aggressive approach. Since the outbreak of the Crimean incident in 2014, most US lawmakers have been concerned about Russia's geostrategic intentions in the Eurasian sector and have imposed multiple rounds of strong economic sanctions on Russia, including a ban on Russian bank bond trading and loans, and a ban on exploration technology cooperation with Russian energy companies; Freeze the assets of Russian officials, ban visa issuance, and freeze online accounts; Revoking the business license of Russian companies, canceling high-tech export licenses, and arms embargoes; Repeated obstruction of the "Beixi 2" project. However, in terms of effectiveness, these sanctions have a greater political purpose and weaker economic "attack power".
2、 The main methods and characteristics of the US and Europe's current round of sanctions against Russia
Recently, with the escalation of the conflict between Russia-Ukraine conflict, the United States has successively issued two administrative orders and four related directives against Russia, and continues to issue sanctions laws and regulations against Russia. The scale, frequency, and scope of deterrence of this sanctions, as well as the extensive implementation of sanctions in collaboration with allies, are the extreme characteristics presented by the US economic sanctions in the context of this war.
Unlike most mechanisms that target specific targets and implement targeted sanctions, this sanction provides a more direct statement of its expected effects, namely cutting off Russian banks from the US financial system, cutting off more than half of Russia's high-tech imports, restricting Russia's access to key technologies, shrinking its industrial base, and ultimately weakening Russia's ability to exert influence on the world stage.
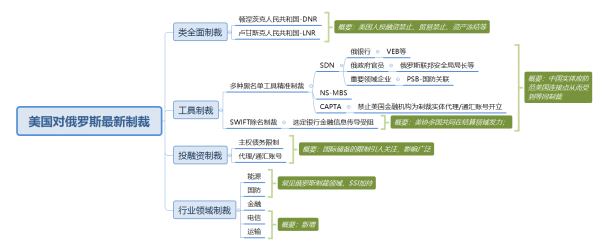
The highly anticipated and most likely to have a comprehensive impact on the Russian economy in this sanctions include:
1. Excluding Russia by leveraging its actual monopoly financial instruments and financial market advantages
On February 26th, the White House of the United States announced that leaders from the European Commission, France, Germany, Italy, the United Kingdom, and Canada have decided to exclude some Russian banks from the Global Interbank Financial Communications Association (SWIFT). This means that Russia has been fully locked down by Western financial markets, and some Russian financial institutions are unable to conduct cross-border transactions, communication, and clearing normally, and cannot obtain new foreign exchange through bonds and corporate financing. Specifically:
The UK announced a ban on Russian state-owned enterprises and private companies in key areas from financing in the UK financial market;
The EU has announced a ban on the listing and provision of services of Russian physical shares on EU trading venues, the acceptance of deposits from Russian nationals or residents exceeding a specific value, and the sale of Euro denominated securities by the EU Central Depository Institution to Russian clients;
The United States prohibits domestic financial institutions from participating in the market for Russian financial services sector bond issuance;
Japan prohibits the Russian government from issuing new sovereign bonds in Japan;
Canada prohibits its citizens from purchasing Russian sovereign debt.
It is reported that such restrictive measures against banks such as the Russian Central Bank are related to the safety and use of over $600 billion in international reserves in Russia. Therefore, the potential impact of these measures has also received high attention from the international community. The above-mentioned sanctions will have a significant impact on the import and export trade, international payments, foreign exchange, and other aspects of Russian banks.
2. Cut off imports from Russia's key supply chain
Looking at the multi departmental coordinated sanctions initiated by the United States, from a broad perspective, export controls targeting items have become an important tool for the Ministry of Commerce to restrict foreign access to US related items. This time, in response to the Russia-Ukraine conflict, BIS, the Bureau of Industry and Security of the United States Department of Commerce, has also simultaneously implemented a series of comprehensive and strict export control measures to limit the development of Russia's defense, aerospace, maritime transport and other key fields to the greatest extent, and tried to cut off the access of key sectors of Russia's industrial infrastructure to any key items related to the United States, including semiconductor, computer, telecommunications, information security equipment, lasers, sensors and other products, To weaken Russia's influence on the Eurasian stage. The new measures include:

The EU will prohibit the sale, supply, transfer, or export of specific refining products and technologies to Russia, and impose restrictions on the provision of related services. The ban is aimed at cracking down on Russia's oil sector, preventing it from upgrading its refineries. The EU will also prohibit the sale of all aircraft, spare parts, and equipment to Russian airlines, and prohibit the provision of insurance, reinsurance, and maintenance services related to these goods and technologies;
The UK has announced new punitive trade and export control restrictions on Russia's high-tech and strategic industries, cracking down on its electronics, telecommunications, and aerospace companies;
The energy, communication, and aviation industries on which the Russian economy relies will face difficulties in upgrading.
Part 2: The Impact of US and European Sanctions on Chinese Enterprises in Russia
1、 Import and export trade field
According to the data of the United States Department of Commerce, the total US exports to Russia in 2020 will be 4.9 billion US dollars, down 15.6% from 2019, and the total US imports from Russia will be 16.8 billion US dollars, down 24.3%.
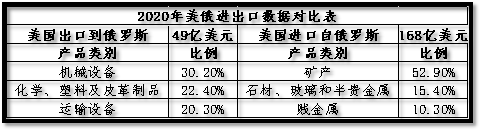
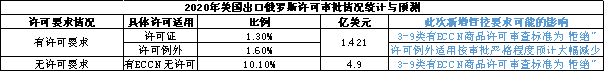
In 2020, out of the $4.9 billion in exports from the United States to Russia, 2.9% (approximately $142.1 million) of goods had corresponding licensing requirements, and about 10% ($490 million) of goods had specific ECCN but no export licensing requirements. According to the revision of the US export management regulations, one of the important changes was the addition of control requirements for categories 3-9 of goods in the commercial control list, and the direct provision of the licensing review standard as "refusal", These policies are quite different from the "inferred refusal" and "case review" licensing policies commonly used previously by the United States Department of Commerce. Therefore, the above amendments will also have a direct impact on Russian imports of US related items. At the same time, the tightening of licensing review in the Russian market may also lead to a significant reduction in the exceptional application of the original license. However, due to the small volume of direct exports from the United States to Russia, the potential impact of the corresponding supply cut-off on the Russian market is also relatively limited.
In 2020, China's imports from the United States amounted to approximately $124.6 billion, while its exports to Russia in the same year amounted to nearly $67.5 billion. Among these export commodities, some are produced in China, and there may also be products produced using American technology, as well as products produced and sold to China by other countries but also containing products produced and ultimately exported using American technology or software. For these products, Russia will also be more generally affected by the new foreign direct product rules introduced by the United States. The United States has also revised its foreign direct product rules to maximize restrictions on Russia's acquisition of any US related items, including items originating in the United States, direct exports from the United States, and items from foreign countries that fall under the jurisdiction of the US EAR based on the aforementioned foreign direct product rules, thereby maximizing the flow of US related items into the Russian market.
2、 Financial banking sector
On February 26th local time, the United States, the European Union, the United Kingdom, and Canada issued a joint statement promising to ensure the exclusion of several "selected" Russian banks from the SWIFT international settlement system. According to the joint statement, the latest sanctions measures will ensure the disconnection of Russian banks from the international financial system, 'damaging their ability to operate globally'. There are currently 466 financial institutions in Russia that are SWIFT members, and this sanction means that Chinese companies in Russia may not be able to communicate safely and effectively with foreign banks through Russian banks, thus preventing cross-border fund payment and settlement.
3、 Supply chain interruption
According to foreign media reports, global computer chip manufacturers, including TSMC, have begun to stop selling products to Russia, and semiconductor manufacturers have expressed their willingness to comply with the law and closely cooperate with government measures. Global Foundries, a chip manufacturer based in Malta, New York, and Intel, based in Santa Clara, California, have suspended delivery of their products to Russia. As more and more companies stop delivering products to Russia, Chinese companies located in Russia face the risk of supply chain disruptions.
Part Three: The Impact of US and European Sanctions on Non Russian Chinese Enterprises with Business Relationships with Russia
1、 From the perspective of export enterprises
According to the latest data released by the Ministry of Commerce of China, the trade volume of goods between China and Russia reached 146.87 billion US dollars in 2021, ranking as Russia's largest trading partner for 12 consecutive years. Among the goods exported by China to Russia in 2021, the top 20 include handheld wireless telephones, automatic data processing equipment, fur clothing, toys, electrical equipment, LCD display panels, small buses, compressors, valves, and lighting devices.
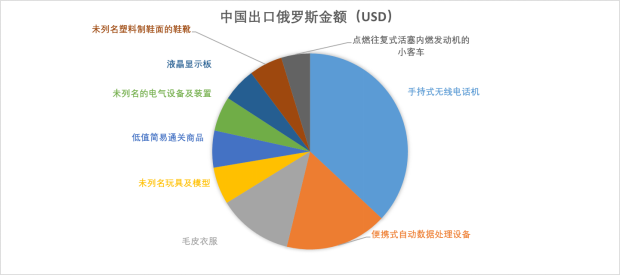
According to the information in the above figure, China's exports to Russia may involve products that are produced using specific US technologies or software and comply with foreign direct product rules, such as products in the chip category. Taking the eighth ranked LCD panel (LCD) export as an example, the LCD industry chain is generally divided into three categories: raw materials and equipment, production and manufacturing, and end products. Most Chinese screen factories are in the middle position, That is, the assembly and production of panels. Since 2018, China has become the region with the largest production capacity of large-sized LCD panels in the world for this type of product. Its application areas include televisions, monitors, laptops, smartphones, and tablets. Although the localization rate of panels has become increasingly high, they are mainly produced in the "processing with supplied materials" mode, which highlights the objective fact of insufficient control over upstream core technologies. For example, there are certain technical barriers for polarizers and color filters, which account for nearly 50% of panel costs. Almost all of them are dominated by Japanese and Korean enterprises. In the field of LCD screen glass alone, Corning in the United States accounts for almost half of the market share. Secondly, in the field of production equipment, the measurement, testing and other production equipment involved in the production of LCD screens are mainly provided by Japan and South Korea.
In the composition of LCD display modules, for example, if the chip market is currently unable to break through the restrictions of the aforementioned export control measures (foreign direct product rules) in the United States, that is, if the destination of the shipment is Russia, but the integrated chip products are produced using American original technology or software (such as EDA software 3D991), and the foreign manufactured products are not EAR99 products, there is a high probability that they cannot be exported to Russia.
2、 From the perspective of import enterprises
The top 10 commodities imported by China from Russia in 2021 include petroleum, crude oil, natural gas, coking coal, iron ore, precious metal ore sand, pine and fir, as shown in the following figure:
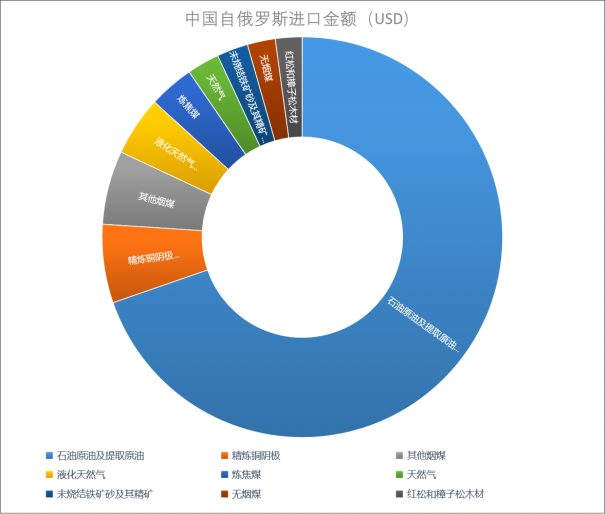
China's import data on energy also reflects that oil, natural gas, and other important goods imported by China from Russia. Although the above sanctions measures are mainly aimed at Americans, they require Americans not to import/invest in energy products originating from Russia, such as oil and natural gas. For Chinese enterprises, attention should be paid to:
1) Not involving US connection points to avoid corresponding sanctions risks, such as not causing Americans to violate the ban on participating in or investing in energy imports, unable to settle in US dollars, etc;
2) Chinese enterprises are also prohibited from engaging in significant transactions or providing substantive assistance for transactions with SDN enterprises, although they do not involve US connection points.
Part 4: Response of Chinese Enterprises
In the context of the Russia-Ukraine conflict, the US sanctions against Russia are frequently updated and show a trend of diversification, with different management and control rules in different fields. Therefore, for Chinese enterprises, it is necessary to ensure their commercial interests, and take into account the application and impact of relevant laws and regulations. Professionals need to help carefully identify the risks in each and deal with them carefully.
1. Risk assessment for specific business areas
As mentioned earlier, although the current situation is constantly escalating, the risk of sanctions against Russian financial institutions has been prevalent for many years. In order to strive to maintain the normal operation and reputation of enterprises, both enterprises and financial institutions need to conduct a thorough assessment of potential risks.
Financial institutions: Since the Crimean crisis in 2014, the United States has launched multiple rounds of economic sanctions against Russia. Due to its important role in financing, financial institutions are often targeted in the first round of sanctions. Therefore, for banks and other financial institutions within the financial system, the previous economic sanctions imposed by the United States on Russia should have already been implemented I have a certain understanding of control measures such as anti money laundering and have gradually developed my own response methods.
Non financial institutions: For enterprises outside the financial system, they face relatively few compliance regulatory restrictions, so their core capabilities in compliance processes, corporate governance, risk assessment, and other aspects will be highlighted. Especially for enterprises involving dual-use items/technologies, how to gain a deeper understanding of Russia's sanctioned entities and global supply chains when facing key regulatory and sanctions concerns in countries and regions such as the United States and Europe It is crucial to truly understand the upstream and downstream partner relationships, such as Know Your Customer (KYC). Providing due diligence on partners and maintaining continuous monitoring of sanctions lists and partners can help stabilize the future business of the enterprise.
Therefore, risk identification of actual business content is the core, which may include but not limited to risk identification of import and export trade items, confirmation of upstream and downstream partner blacklists, risk sorting of trading countries and industry sectors, etc. At the same time, commercial and legal risks should be comprehensively considered in conjunction with business scenarios.
2. Continuous attention and monitoring of regulatory and sanctions trends
China and Russia have established a close strategic partnership since 2014. For Chinese companies, especially those with close trade ties with Russia and financial institutions, special attention should be paid to Russian regulation and sanctions, to avoid being seen as "evading" the risk of triggering sanctions by providing substantive assistance or corresponding convenience to sanctioned Russian entities or transactions.
However, in view of the ever-changing international situation, the relevant policies in the field of export control and economic sanctions are also changing. Accurate judgment and prediction of the international situation and the policies of the countries involved in the company's business will help enterprises adjust their strategic planning in advance and prepare for response measures. The analysis and research of the international situation and policies are not purely legal issues, but more related to politics, diplomacy, and other related issues. Therefore, the Cross border Sanctions and Export Control Research Center of Beiwai fully utilizes its political, diplomatic, language advantages, and regional and national research advantages to conduct in-depth research on export control and economic sanctions related issues in different countries, and can also delve into the core think tanks of relevant countries, Conduct scientific analysis and prediction of the trends of export control and economic sanctions related policies, and combine the practical experience of a professional lawyer team in the legal field. On the basis of integrating political diplomacy, business management, and legal risk prevention and control, provide comprehensive consulting services and assistance to the company, in order to achieve early layout.
3. Actively respond to different fields and personal situations
The US sanctions against Russia involve a variety of subjects, with a focus on government departments, government officials, and key Russian industry enterprises. However, there are significant differences in the risk points and response methods that enterprises in different fields need to pay attention to.
For example, for enterprises that need to conduct investment and financing in Russia, they need to conduct a sanctions list verification on the target company, and evaluate investment and financing risks based on whether they fall into the specific sanctions list and the corresponding sanctions measures on the list. For example, if non US persons engage in significant transactions or provide substantial assistance with SDN entities, the trading entity may be subject to sanctions. Some regulations may also trigger sanctions against non Americans for aiding and facilitating transactions.
For shipping companies, the United States is well aware of the dependence of international shipping trade on the US financial system and the US dollar. OFAC's focus on shipping due diligence specifically includes providing guidance to shipowners, operators, brokers, shippers, flag registrars, port operators, shipping companies, freight forwarders, classification service providers, commodity traders, insurance companies, and financial institutions, Therefore, shipping companies not only need to understand customers and counterparties, but also have an essential understanding of industry information such as full cycle monitoring of ships, supply chain due diligence, shipowners, and shipowner clubs.
4. Industry Alliance and Professional Legal Counseling
Faced with the normalization, diversification, and complexity of regulatory and sanctions measures in countries such as the United States and Europe, enterprises need to master a large amount of resources and technical skills to effectively judge and respond, including industry resources and matching legal service resources. We suggest that relevant enterprises establish corresponding local industry compliance alliances with other enterprises in the same industry field and enterprises related to Russian business, strengthen cooperation with professional institutions in compliance response, regularly conduct discussions with the same functional departments and industry chains in the industry, and conduct legal risk assessment and professional guidance with compliance experts. While reducing the burden of enterprise compliance, It can help enterprises gain a deeper understanding of relevant legal risks and find universally applicable risk management and compliance solutions.
In view of the limited space, we only conduct principled analysis on the risk impact and response strategies brought by the control and sanctions measures of the Russia-Ukraine conflict in this article. In practice, the risks faced by enterprises in different fields and different industrial chain ports and their responses are different. If there is any need, you can contact us at any time to make further analysis and answers based on the actual situation.

Expert Introduction

Guo Huan
Going Out to Think Tank (CGGT) Appointed Legal Expert
Partner in Cross border Regulatory Business at Jindu Law Firm
In recent years, I have led or participated in a large number of comprehensive projects in the field of corporate compliance, especially in the areas of export control and economic sanctions. I have assisted various high-tech enterprises, including aerospace, communication, electronics, etc., in establishing an export control compliance internal control system (ECP), focusing on cross-border transactions and overseas compliance system construction, customs inspection, and customs administrative/criminal case response. My business areas include corporate compliance Export controls and economic sanctions, international trade and regulatory legal services centered around customs and foreign exchange management.

Zhou Xinyu
School of Global Governance and Advanced Studies, Beijing International Studies University
Professor and doctoral supervisor
Beijing International Studies University Cross border Sanctions and Export Control Research Center
Co Director and Secretary General
Professor Zhou Xinyu is one of the representative scholars in the field of public diplomacy research in China, a famous corporate public diplomacy expert, specializing in the study of public diplomacy discourse and non-state actors in international relations. He has a profound theoretical foundation in the research of macro policies in the field of transnational sanctions and export control, and is a professional expert in solar energy, semiconductor, logistics, unmanned aerial vehicles Enterprises in various fields such as biopharmaceuticals have provided relevant policy consultation and risk assessment services. Professor Zhou is also the Deputy Director and Secretary General of the public diplomacy Research Center of Beijing Foreign Studies University, an academic consultant of the China public diplomacy Association, and a special commentator of China Radio International.

Chen Qichao
Cross border regulatory business consultant at Jindu Law Firm
Business Area: Export Control and Economic Sanctions
Mr. Chen Qichao has focused on the research of export control regulations and the establishment and implementation of the Export Compliance Internal Control System (ECP) in his work over the past decade. Provide export control related consulting services for well-known enterprises in China, the United States, and Japan, assist enterprises in classifying export items, applying for licenses, building internal compliance systems, conducting export control training, and auditing work. I have rich practical experience in the fields of export control and economic sanctions.
Institutional Introduction
Cross border Sanctions and Export Control Research Center
The center is established at the School of International Business and School of International Relations of Beijing International Studies University. It employs scholars from other universities and research institutions, outstanding lawyers from the economic sanctions and export control compliance team of Beijing Jindu Law Firm, and professionals from relevant enterprises, among other elite forces. The center aims to focus on cross-border sanctions and export controls, customs supervision, international trade, etc, Combining the important research achievements accumulated by Beijing International Studies University in international relations, international economy, and other fields with the rich practical experience accumulated by foreign lawyers in cross-border trade services, we will gather political, legal, and commercial forces to promote China's export control legal construction, promote international exchange and cooperation in the fields of import and export control and economic sanctions, provide assistance for the development of high-tech enterprises at home and abroad, and cultivate professional talents in related fields We will play an active role in strengthening legal research and legal services related to export controls and economic sanctions, with the aim of interpreting and judging relevant policy trends and legislative trends from a more macro perspective. While actively conducting cutting-edge academic research, we will also provide strong technical support for the field of legal practice.
Extended Reading
Cross border Compliance Observation | Another Precise Strike by the US on Chinese Enterprises - The Dilemma and Countermeasures of Unverified List (UVL) Enterprises
Cross border Compliance Observation | How Chinese Enterprises Respond to the US Listing 33 Chinese Entities on the Export Control "Unverified List"
Cross border compliance observation | How can the United States remove 33 more Chinese entities from the 'unverified list'?
Cross border compliance observation | How do companies respond to investigations and accusations of "forced labor" overseas? (Part 2)
Cross border compliance observation | How do companies respond to investigations and accusations of "forced labor" overseas? (Part 1)
Cross border Compliance Observation | Analysis of Long Arm Jurisdiction Policies in the United States and Suggestions for Response Measures to Combat "White Collar Crime"
Cross border Compliance Observation | The Dilemma and Response Strategies of China's Biomedical Industry Faced with US Export Controls
China US Observation | How to Avoid the Risk of "Shock" Interruption in the Industrial Chain of Photovoltaic Enterprises Faced with US Sanctions
Observation of China and the United States | Reshaping the Supply Chain: Exploring the Dilemmas and Breakthroughs of China's Semiconductor Industry (Part 1)
Observation of China and the United States | Reshaping the Supply Chain: Exploring the Dilemmas and Breakthroughs of China's Semiconductor Industry (Part 2)
US Policy Insight | Cross border Control from the Perspective of "Military Civilian Integration" • Sanctions and Risk Control Compliance - Detailed Explanation of Response Strategies to the Military Related List in China
US Policy Insight | Cross border Control from the Perspective of "Military Civilian Integration" • Sanctions and Risk Control Compliance - Detailed Explanation of the US Military Related List to China
US Policy Insight | China's Photovoltaic Industry Faces US Sanctions, How to Take the Lead in Crisis
Insight into US Policy | Following Cotton, Xinjiang Photovoltaics has also been labeled as "forced labor", and how Chinese enterprises respond to US sanctions


